Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
山 正樹*; 松尾 衛; 加藤 岳生*
Physical Review B, 107(17), p.174414_1 - 174414_15, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically consider the effect of vertex correction on spin pumping from a ferromagnetic insulator (FI) into a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) in which the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions coexist. The Gilbert damping in the FI is enhanced by elastic spin-flipping or magnon absorption. We show that the Gilbert damping due to elastic spin-flipping is strongly enhanced by the vertex correction when the ratio of the two spin-orbit interactions is near a special value at which the spin relaxation time diverges while that due to magnon absorption shows only small modification. We also show that the shift in the resonant frequency due to elastic spin-flipping is strongly enhanced in a similar way as the Gilbert damping.
前川 禎通; 吉川 貴史*; 中堂 博之; 家田 淳一; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:96.84(Physics, Applied)Along with the progress of spin science and spintronics research, the flow of electron spins, i.e., spin current, has attracted interest. New phenomena and electronic states were explained in succession using the concept of spin current. Moreover, as many of the conventionally known spintronics phenomena became well organized based on spin current, it has rapidly been recognized as an essential concept in a wide range of condensed matter physics. In this article, we focus on recent developments in the physics of spin, spin current, and their related phenomena, where the conversion between spin angular momentum and different forms of angular momentum plays an essential role. Starting with an introduction to spin current, we first discuss the recent progress in spintronic phenomena driven by spin-exchange coupling: spin pumping, topological Hall torque, and emergent inductor. We, then, extend our discussion to the interaction/interconversion of spins with heat, lattice vibrations, and charge current and address recent progress and perspectives on the spin Seebeck and Peltier effects. Next, we review the interaction between mechanical motion and electron/nuclear spins and argue the difference between the Barnett field and rotational Doppler effect. We show that the Barnett effect reveals the angular momentum compensation temperature, at which the net angular momentum is quenched in ferrimagnets.
船戸 匠*; 山影 相*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 106(21), p.214420_1 - 214420_7, 2022/12
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:17.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically study the generation of spin current due to a surface acoustic wave (SAW) in a superconductor. We model an  -wave superconductor as the mean-field Hamiltonian and calculate spin current generated via spin-vorticity coupling based on quantum kinetic theory. The results suggest that the spin current can be driven in a single-superconductor layer, and our estimation suggests that the detectable magnitude of the spin current can be generated in aluminum. Our proposal may contribute to the advancement of spin transport in superconductors from application and fundamental physics aspects.
-wave superconductor as the mean-field Hamiltonian and calculate spin current generated via spin-vorticity coupling based on quantum kinetic theory. The results suggest that the spin current can be driven in a single-superconductor layer, and our estimation suggests that the detectable magnitude of the spin current can be generated in aluminum. Our proposal may contribute to the advancement of spin transport in superconductors from application and fundamental physics aspects.
船戸 匠*; 加藤 岳生*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 106(14), p.144418_1 - 144418_10, 2022/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:34.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study spin pumping into an anisotropic Dirac electron system induced by microwave irradiation to an adjacent ferromagnetic insulator theoretically. We formulate the Gilbert damping enhancement due to the spin current flowing into the Dirac electron system using second-order perturbation with respect to the interfacial exchange coupling. As an illustration, we consider the anisotropic Dirac system realized in bismuth to show that the Gilbert damping varies according to the magnetization direction in the ferromagnetic insulator. Our results indicate that this setup can provide helpful information on the anisotropy of the Dirac electron system.
 -wave superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator bilayer systems
-wave superconductor/ferromagnetic insulator bilayer systems大湊 友也*; 山影 相*; 加藤 岳生*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 105(20), p.205406_1 - 205406_7, 2022/05
被引用回数:8 パーセンタイル:77.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) modulation in  -wave superconductor (SC)/ferromagnetic insulator (FI) bilayer systems theoretically. The modulation of the Gilbert damping in these systems reflects the existence of nodes in the
-wave superconductor (SC)/ferromagnetic insulator (FI) bilayer systems theoretically. The modulation of the Gilbert damping in these systems reflects the existence of nodes in the  -wave SC and shows power-law decay characteristics within the low-temperature and low-frequency limit. Our results indicate the effectiveness of the use of spin pumping as a probe technique to determine the symmetry of unconventional SCs with high sensitivity for nanoscale thin films.
-wave SC and shows power-law decay characteristics within the low-temperature and low-frequency limit. Our results indicate the effectiveness of the use of spin pumping as a probe technique to determine the symmetry of unconventional SCs with high sensitivity for nanoscale thin films.
山 正樹*; 立野 雅大*; 加藤 岳生*; 松尾 衛
Physical Review B, 104(5), p.054410_1 - 054410_9, 2021/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically consider spin pumping in a junction between a ferromagnetic insulator (FI) and a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) in which the Rashba and Dresselhaus spin-orbit interactions coexist. Using second-order perturbation theory, we derive an increase in linewidth in the case of an interfacial exchange coupling in a ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) experiment. We clarify how the enhancement of Gilbert damping depends on the resonant frequency and spin orientation of the FI. We show that this setup of an FMR experiment can provide information on the spin texture of 2DEG at the Fermi surface.
亀田 麻衣*; 廣部 大地*; 大門 俊介*; 塩見 雄毅*; 高橋 三郎*; 齊藤 英治
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 476, p.459 - 463, 2019/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:4.76(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nonlinear effects of spin pumping have been investigated by numerically calculating the temporal evolution of the magnon number affected by three- and four-magnon interactions. We showed that the three-magnon interaction gives rise to the enhancement of spin-pumping spin current. We also found that the four-magnon interaction in combination with the three-magnon interaction can be responsible for the experimentally observed low-frequency oscillation of spin current.
塩見 雄毅*; Lustikova, J.*; 渡辺 真悟*; 廣部 大地*; 高橋 三郎*; 齊藤 英治
Nature Physics, 15(1), p.22 - 26, 2018/10
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:74.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Various spintronic phenomena originate from the exchange of angular momentum between the spin of electrons and other degrees of freedom in crystalline materials. Many degrees of freedom, such as magnetization and mechanical motion, have already been united into this exchange framework. However, the nuclear spin -a key angular momentum- has yet to be incorporated. Here we observe spin pumping from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), in which nuclear spin dynamics emits a spin current, a flow of spin angular momentum of electrons. By using the canted antiferromagnet MnCO , in which typical nuclear spin-wave formation is established due to the reinforced hyperfine coupling, we find that a spin current is generated from an NMR. Nuclear spins are indispensable for quantum information technology and are also frequently used in various sensors, such as in magnetic resonance imaging. The observed NMR spin pumping allows spin-current generation from nuclei and will enable spintronic detection of nuclear spin states.
, in which typical nuclear spin-wave formation is established due to the reinforced hyperfine coupling, we find that a spin current is generated from an NMR. Nuclear spins are indispensable for quantum information technology and are also frequently used in various sensors, such as in magnetic resonance imaging. The observed NMR spin pumping allows spin-current generation from nuclei and will enable spintronic detection of nuclear spin states.
白 怜士*; 田代 隆治*; 中山 裕康*; 家田 淳一; 圓谷 志郎; 境 誠司; 安藤 和也*
Applied Physics Express, 8(7), p.073009_1 - 073009_3, 2015/07
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:18.63(Physics, Applied)Ni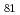 Fe
Fe /Pt二重層の境界面に、単層グラフェン(SLG)を挿入するとスピンポンピングが強力に抑制されることを見いだした。Ni
/Pt二重層の境界面に、単層グラフェン(SLG)を挿入するとスピンポンピングが強力に抑制されることを見いだした。Ni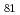 Fe
Fe /Pt二重層におけるスピンポンピングは、強磁性層の磁化緩和を促進させる。このことは、強磁性共鳴線幅のマイクロ波周波数依存性により定量的に評価される。我々は、このスピンポンピングによる磁化緩和の促進が、Ni
/Pt二重層におけるスピンポンピングは、強磁性層の磁化緩和を促進させる。このことは、強磁性共鳴線幅のマイクロ波周波数依存性により定量的に評価される。我々は、このスピンポンピングによる磁化緩和の促進が、Ni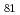 Fe
Fe /SLG/Pt三重層において消失することを示す。本成果は、単一原子層によってスピンポンピングが遮断されることを示しており、金属系のスピンポンピングにおける界面短距離スピン交換結合の重要性を明らかにするものである。
/SLG/Pt三重層において消失することを示す。本成果は、単一原子層によってスピンポンピングが遮断されることを示しており、金属系のスピンポンピングにおける界面短距離スピン交換結合の重要性を明らかにするものである。
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
The two-dimensional quantum spin Hall insulator (2D QSHI) is the most primitive but quite important realization of topological insulator. It shows the helical edge states protected by time-reversal symmetry, whereas the quantized spin Hall conductivity in the bulk. In the present work, we theoretically investigate the spin pumping from a precessing ferromagnet into a 2D QSHI thoroughly from the adiabatic to nonadiabatic regimes, both analytically and numerically. We analytically treat the dynamics of the edge-state electrons coupled to the precessing ferromagnet by the Floquet theory, and derive the pumped current as a function of the exchange energy and the precession frequency. We find that a heat bath for the edge electrons governs the transition between the adiabatic and nonadiabatic regime: when the edge electrons are coupled with a heat bath, their spin and energy can dissipate into the bath by a certain rate, eventually reaching a periodic steady state. The pumped current on the becomes quantized when the exchange energy exceeds the dissipation rate. We also calculate the edge current numerically on the 2D lattice model, and find that the bulk states in the QSHI effectively serves as the heat bath for the edge electrons.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). QSHI is a topological insulator in 2D exhibiting gapless helical edge stats, which are responsible for the quantized spin Hall conductivity. Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on dynamical spin-to-charge conversion at the edge of a quantum spin Hall insulator (QSHI), namely a two-dimensional topological insulator with helical edge states. Interconversion between spin- and charge-related quantities has been a key idea in making use of magnetic materials, especially in the context of spintronics. QSHI is a typical system showing a universal charge-to-spin conversion behavior, namely the quantum spin Hall effect, whereas the spin-to-charge conversion therein is still not clearly understood. At a lateral heterojunction of a ferromagnet (FM) and a QSHI, it has been theoretically demonstrated that magnetization dynamics induces a charge current along the edge of QSHI; however, its mechanism from the viewpoint of spin-to-charge conversion still remains to be clarified. In order to understand the spin transfer and the spin-to-charge conversion mechanism in QSHI, we investigate the many-body dynamics of the electrons under the magnetization dynamics at the QSHI-FM junction. We analytically treat the electron dynamics in terms of the Floquet-Keldysh formalism, and compare two physical quantities present on the edge: the spin injection rate from the FM into the QSHI, and the charge current induced along the edge. Whereas the edge current seen in the previous works is reproduced, we find that it is not proportional to the spin injection rate, especially when the exchange interaction at the junction is strong enough. This relation implies that the spin-to-charge conversion in this system cannot be considered as the inverse spin Hall effect, while it can be rather seen as the inverse Edelstein effect, in which an electron spin accumulation at the junction is converted to a charge current. We also focus on the energy transfer at the junction, and interpret this phenomenon in terms of magnon exchange.